1. bridge的VLAN filter功能
参考: https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2017/09/14/vlan-filter-support-on-bridge#
1.1. old way
如果用linux bridge配置带vlan的网络, 以前的做法是创建多个br, 每个br对应一个vlan, 例如: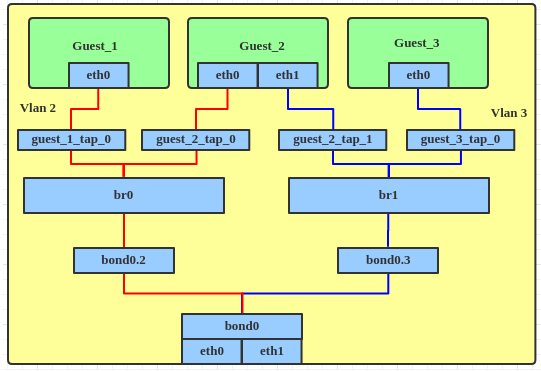
命令:
Create a bond device.
# ip link add bond0 type bond
# ip link set bond0 type bond miimon 100 mode balance-alb
# ip link set eth0 down
# ip link set eth0 master bond0
# ip link set eth1 down
# ip link set eth1 master bond0
# ip link set bond0 up
Create VLANs on bond. We need to create more VLANs if dictated by requirements.
# ip link add link bond0 name bond0.2 type vlan id 2
# ip link set bond0.2 up
# ip link add link bond0 name bond0.3 type vlan id 3
# ip link set bond0.3 up
Add a bridge device, to which we can attach the VLAN interface.
# ip link add br0 type bridge
# ip link set bond0.2 master br0
# ip link set br0 up
# ip link add br1 type bridge
# ip link set bond0.3 master br1
# ip link set br1 up
Attach tap device to bridge.
# ip link set guest_1_tap_0 master br0
# ip link set guest_2_tap_0 master br0
# ip link set guest_2_tap_1 master br1
# ip link set guest_3_tap_0 master br1
1.2. 使用VLAN filter功能
This feature was introduced in Linux kernel 3.8 and was added to RHEL in version 7.0. Let's take an example that is widely used in virtualization: different subnets on a bridge with bond load balance.
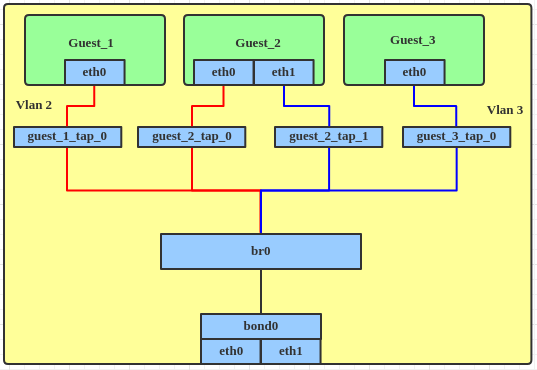
Create a bond device, the same as above.
# ip link add bond0 type bond
# ip link set bond0 type bond miimon 100 mode balance-alb
# ip link set eth0 down
# ip link set eth0 master bond0
# ip link set eth1 down
# ip link set eth1 master bond0
# ip link set bond0 up
Create the bridge interface, enable VLAN filter and attach the bond interface to the bridge directly.
# ip link add br0 type bridge
# ip link set br0 up
# ip link set br0 type bridge vlan_filtering 1
# ip link set bond0 master br0
Attach the tap device to the bridge.
# ip link set guest_1_tap_0 master br0
# ip link set guest_2_tap_0 master br0
# ip link set guest_2_tap_1 master br0
# ip link set guest_3_tap_0 master br0
Set the tap interface with the VLAN filter.
# bridge vlan add dev guest_1_tap_0 vid 2 pvid untagged master
# bridge vlan add dev guest_2_tap_0 vid 2 pvid untagged master
# bridge vlan add dev guest_2_tap_1 vid 3 pvid untagged master
# bridge vlan add dev guest_3_tap_0 vid 3 pvid untagged master
# bridge vlan add dev bond0 vid 2 master
# bridge vlan add dev bond0 vid 3 master
To dump the VLAN information from the bridge interface.
# bridge vlan show
port vlan ids
bond0 1 PVID Egress Untagged
2
3
br0 1 PVID Egress Untagged
guest_1_tap_0 1 Egress Untagged
2 PVID Egress Untagged
guest_2_tap_0 1 Egress Untagged
2 PVID Egress Untagged
guest_2_tap_1 1 Egress Untagged
3 PVID Egress Untagged
guest_3_tap_0 1 Egress Untagged
3 PVID Egress Untagged
2. docker内部ping 宿主机外部ip
2.1. docker内eth0
mac: 02:42:ac:11:00:02
ip: 172.17.0.2/16
默认路由: default via 172.17.0.1 dev eth0
2.2. docker0网桥
mac: 02:42:29:ac:5c:40
ip: 172.17.0.1/16
2.3. host eth0
mac: fa:16:3e:cf:b4:34
ip: 192.168.0.14/24
默认路由: default via 192.168.0.1 dev eth0
对外ip: 10.182.105.138
2.4. 在docker内ping 10.182.105.138
现象: 能ping通
2.4.1. 过程第一步
在docker0抓包看到:
发送icmp请求
02:42:ac:11:00:02 > 02:42:29:ac:5c:40
172.17.0.2 > 10.182.105.138: ICMP echo request
回复icmp响应:
02:42:29:ac:5c:40 > 02:42:ac:11:00:02
10.182.105.138 > 172.17.0.2: ICMP echo reply
所以第一步: docker内部协议栈没有找到138的路由, 走默认路由, 即docker0网桥, 目的ip为138不变, mac地址改为docker0的mac地址
2.4.2. 过程第二步
现在报文来到host的docker0网桥上, 但依然没有找到138的路由. 在通过默认路由前, 需要做NAT转换: 把内网ip(172.17.0.2)换成host ip(192.168.0.14)
#这里很有意思的出现了2次icmp request
#第一次是host ip发给138
fa:16:3e:cf:b4:34 > fa:16:3e:36:da:c0
192.168.0.14 > 10.182.105.138: ICMP echo request
#第二次是138发给host ip
fa:16:3e:36:da:c0 > fa:16:3e:cf:b4:34
10.182.105.138 > 192.168.0.14: ICMP echo request
#以上出现两次request的原因是, 138和192.168.0.14是同一个主机.
#类似的, icmp reply也有两个
fa:16:3e:cf:b4:34 > fa:16:3e:36:da:c0
192.168.0.14 > 10.182.105.138: ICMP echo reply
fa:16:3e:36:da:c0 > fa:16:3e:cf:b4:34
10.182.105.138 > 192.168.0.14: ICMP echo reply
2.4.3. 第三步
给192.168.0.14的icmp echo reply: 10.182.105.138 > 192.168.0.14
经过NAT转换为:10.182.105.138 > 172.17.0.2, 协议栈查到172.17.0.2走docker0这个interface, 随后这报文被送到docker内部的ping程序.
2.5. 在docker内ping 192.168.0.14
192.168.0.14即host的eth0的ip
能ping通, 但在host的eth0抓不到包. 说明报文没有从eth0口出来.
从docker0能抓到包
02:42:ac:11:00:02 > 02:42:29:ac:5c:40
172.17.0.2 > 192.168.0.14: ICMP echo request
02:42:29:ac:5c:40 > 02:42:ac:11:00:02
192.168.0.14 > 172.17.0.2: ICMP echo reply
说明报文在docker0网桥的协议栈中, 就知道这个icmp request报文是可以本机处理的, 然后就处理了.
3. linux网桥 veth 等等
3.1. ip netns 网络名字空间
创建网络空间:
# ip netns add ns1
查看网络空间:
# ip netns list
删除网络空间:注意网络空间有引用计数, 最后一个user删除才真正删除
# ip netns del ns1
进入网络空间执行命令:
# ip netns exec ns1 `command`
ip netns ls能看到同名的netns
netns的特性是在外面用ip netns exec命令进入netns空间看, 比如sudo ip netns exec setup_standalone_board_0_1fg247_yingjieb ip a, 和在docker实例里面看的结果, 是一模一样的.
netns是一个新的网络栈的拷贝, 有独立的路由, 规则, 和网络设备.
man ip netns里面说, 一个有名子的netns对应/var/run/netns/NAME目录下的NAME文件, 打开这个文件并传入setns系统调用, task就关联到这个netns了.
ip netns exec自动完成上述netns文件关联到进程的动作, 所以执行的命令是在指定的netns里面执行的.
ip netns set NAME NETNSID - assign an id to a peer network namespace
#看目标PID对应的netns
ip netns identify [PID] - Report network namespaces names for process
#看目标netns里面有哪些PID
ip netns pids NAME - Report processes in the named network namespace
ip netns monitor - Report as network namespace names are added and deleted
ip netns list-id - list network namespace ids (nsid)
上面提到, 有的netns是name, 有的是id, 它们有什么关系吗? --可以是一一对应关系: 下面不管是list还是list-id命令, 都能打印name和id的关系
bash-5.0# ip netns list-id
nsid 0
nsid 1 (iproute2 netns name: pcta_0)
nsid 2 (iproute2 netns name: lt_1)
bash-5.0# ip netns list
dhcpd_1
dhcpd_0
pcta_0 (id: 1)
lt_1 (id: 2)
3.2. veth
veth是个驱动, 可以用来创建虚拟网络设备对. veth总是成对出现, 用来连接网络的两端, 从一端来的报文总是立即被另一端接收.ip link add <p1-name> type veth peer name <p2-name>
上面命令创建了p1-name和p2-name做为veth的两端.
这时候把其中的一端move到netns中, 就能在两个netns间通信了:ip link set <p2-name> netns <p2-namespace>
用ethtool -S或者直接ip link就能看到对应关系
4. docker网络
docker网络文档写的很好: https://docs.docker.com/network/
有以下几种:
- bridge: 最常见的模式. 容器通过bridge连接到host, host提供iptable的规则可以隔离容器, 但又能上外网
又可以分为默认网桥(docker0)和自定义网桥. 自定义网桥有些高级特性
- 自定义网桥有自动DNS解析
- 容器可以动态的接入和断开自定义网桥
- host: 容器直接使用host网络
- overlay: 不同host之间overlay
- macvlan: 让容器的mac看起来像是网络上的物理接口. 就是说报文在host的协议栈发现mac是容器的, 直接投递给容器, 而不是交给网桥路由(个人理解).
- bridge模式
$ docker network create -d macvlan \ --subnet=172.16.86.0/24 \ --gateway=172.16.86.1 \ -o parent=eth0 pub_net - trunk模式
$ docker network create -d macvlan \ --subnet=192.168.50.0/24 \ --gateway=192.168.50.1 \ -o parent=eth0.50 macvlan50
- bridge模式
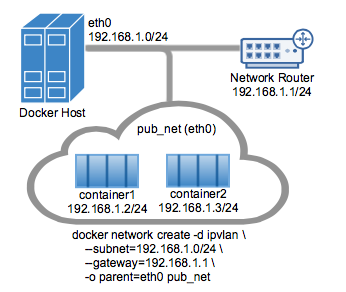
- ipvlan: 感觉是一个轻量的网络虚拟化实现: 不用网桥, 而是绑定到host的物理口eth, 或eth的vlan比如eth.10. 可以是l2模式也可以是l3模式.
支持802.1q trunk模式# IPvlan (-o ipvlan_mode= Defaults to L2 mode if not specified) $ docker network create -d ipvlan \ --subnet=192.168.1.0/24 \ # Start a container on the db_net network $ docker run --net=db_net -it --rm alpine /bin/sh # NOTE: the containers can NOT ping the underlying host interfaces as # they are intentionally filtered by Linux for additional isolation.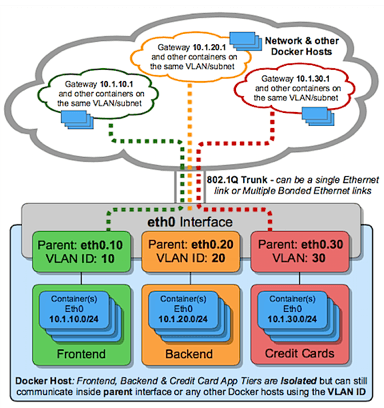
4.1. docker网桥命令
docker network list
docker network create my-net
$ docker create --name my-nginx \
--network my-net \
--publish 8080:80 \
nginx:latest
docker network connect my-net my-nginx
docker network disconnect my-net my-nginx
$ docker network inspect bridge
4.2. docker iptable
docker会修改host的iptable, 加了两个chain:
- DOCKER: 所有的默认规则加在这个chain里
- DOCKER-USER: 在DOCKER chain之前, 用户可以配置, 比如配置除了192.168.1.1的报文都丢弃.
iptables -I DOCKER-USER -i ext_if ! -s 192.168.1.1 -j DROP